
Note that various CDR3 amino acid lengths are present in the library. ( B) Comparison between the designed diversity set for every amino acid position in the CDR3 region with the effective diversity observed after sequencing 2500 clones using NGS. Amino Acid are indicated in single letter code. The position of each amino acid is indicated (CDR1 1 CDR1 2 etc). ( A) Comparison between relative amino acid frequencies in CRD1 and CDR2 observed from 250 llama VHH isolated from a naïve library (llama), the rationally designed (Designed) and the effective diversity in the synthetic library (Nali-H1) as computed after sequencing of 2500 clones using NGS. Living cells were imaged after 24 hr and showed that the hs2dAb recognized its intracellular target lamin. ( D) The anti-lamin based on the two scaffolds were transiently expressed in HeLa cells as GFP fusion. ( C) Immunofluorescence of HeLa cells with recombinant antibody in both scaffolds labeling the nuclear rim structure characteristic of the nuclear lamina.
#Scaffold protein h1 serial
Serial dilutions of supernatant were revealed with an anti-His tag antibody or an anti-human Fc antibody. coli supernatant or as fusions with a human Fc domain and secreted by CHO cells ( Moutel et al., 2009). ( B) Dot blot analysis of the production of both scaffolds either as single domain antibodies in E. Two bands are visible, one for wild-type pIII and one for the pIII fusion with single domain antibodies. ( A) Phages presenting each scaffolds (sdAbD 10 and hs2dAb) bearing anti-lamin CDRs were produced in E.coli and supernatant were detected in Western Blot with an anti-pIII antibody (NEB). ( C) HeLa cells expressing a GFP fusion of sdAb D10 showing homo-dispersed fluorescence (right) compared to typical randomly chosen aggregating llama VHH considered as non intrabody (left). The soluble supernatant containing the VHH was then concentrated using Amicon filters (lane 3). Periplasmic extract was subjected to heat treatment at 70☌ and insoluble proteins were pelleted by centrifugation (lane 2). Clone D10 was expressed in E.coli and protein secreted in the periplasm were extracted (lane 1). ( B) Analysis of heat purified sdAb D10 by SDS-PAGE. Serial dilution of E.coli culture expressing VHH. Bottom: Relative colony growth of selected VHH (GFP4 and Lam1 chromobodies, or thermostable Re3) on chloramphenicol selection medium (Cam). Top: scheme of the construct expressed from pAO-VHH-CAT-HA vector. ( A) Chloramphenicol acetyl transferase carboxy terminal fusion is a folding reporter allowing for the selection of soluble amino terminal VHH. The NaLi-H1 was then screened in various conditions and diversity, efficacy, versatility and affinity evaluated. Quality control was carried out using Sanger sequencing of 315 randomly picked clones and large scale sequencing of 56 000 clones. Gene synthesis (using a tri-nucleotide approach) was ordered, synthetic sequences cloned into the novel pHEN2+ vector, transformed into bacteria and plated on 430 15 cm plates. Finally, the pHEN2 vector was improved by implementing a triple myc tag and inserting a toxic gene (ccdb) to ensure low frequency of empty clones during library construction (6). 4 sizes (9, 12, 15 and 18 amino acids) were chosen for CDR3. A fixed size of 7 aa was chosen for the CDR1 and CDR2. Usability and efficacy of the novel scaffolds (VHH and humanized) were then confirmed evaluating their display on phage, expression in CHO cells and use as intrabodies (3).In silico design was completed analyzing natural CDR diversity (4) and using this information to design synthetic CDRs. A consensus was derived and mutations were introduced to humanize the scaffold (2).
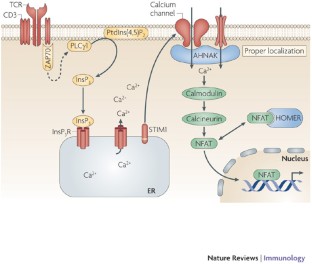
(i) A novel scaffold was defined by selecting a set of robust nanobodies using a CAT fusion assay (1). The development of the NaLi-H1 library followed three lines of optimization.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
